
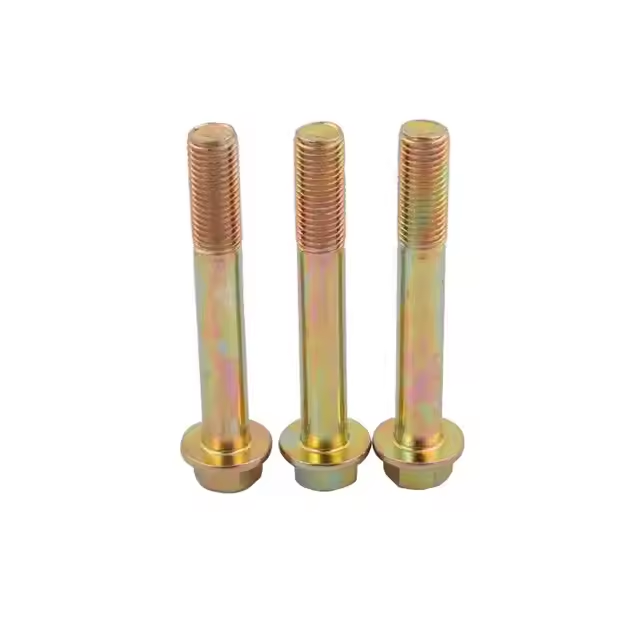
Lag bolts, also known as lag screws, are heavy-duty fasteners designed to join wood together. They are characterized by their pointed tips and coarse threads, which allow them to bite deeply into wood, creating a strong and secure hold. This guide explores everything you need to know before you buy lag bolts for wood, including types, sizes, materials, installation techniques, and factors to consider when making your purchase.Understanding Lag BoltsWhat are Lag Bolts?Lag bolts are large screws typically used to fasten heavy materials, particularly wood, to other materials, including wood, concrete, or metal. Unlike machine screws which require a nut, lag bolts create their own mating thread in pre-drilled holes. The term 'lag' refers to their historical use in fastening wooden lags used in barrel making, thus the name has stuck even with widespread use in other applications.Anatomy of a Lag BoltUnderstanding the different parts of a lag bolt can help you choose the right one for your project: Head: The head is the part that is driven into the material. Common head types include hex, square, and round. Shank: The unthreaded portion of the bolt below the head. Thread: The coarse, pointed threads that grip the wood. Point: The sharp tip that aids in starting the bolt.Types of Lag BoltsHex Head Lag BoltsHex head lag bolts are the most common type. They are easily driven with a wrench or socket.Square Head Lag BoltsSquare head lag bolts provide a more secure grip for the wrench but are less common than hex heads. They are often used in older construction or restoration projects.Round Head Lag BoltsRound head lag bolts, also known as carriage bolts, are used for a more finished appearance and are often used with a washer.Choosing the Right Size and MaterialDetermining the Correct SizeThe size of the lag bolt you need depends on the thickness of the materials you are joining and the load it needs to bear. Here's a general guideline: Length: The bolt should be long enough to penetrate at least half the thickness of the receiving material. For example, if you are fastening a 2-inch thick piece of wood to another, the bolt should be at least 3 inches long (2 inches + 1 inch). Diameter: The diameter depends on the load. Thicker bolts provide more holding power. Common diameters range from 1/4 inch to 3/4 inch.Materials: Steel, Stainless Steel, and MoreLag bolts are available in various materials, each with its own advantages: Steel: Standard steel lag bolts are suitable for general use. Often zinc plated for corrosion resistance. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel lag bolts offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for outdoor applications and marine environments. Galvanized Steel: Galvanized steel lag bolts are coated with zinc to provide corrosion resistance. They are a good option for outdoor projects where stainless steel is not necessary. Hebei Muyi Import&Export Trading Co.,Ltd provides various materials of lag bolts, welcome to visit their website for more information.Installation Guide: How to Use Lag Bolts CorrectlyStep 1: Pre-Drilling the Pilot HoleAlways pre-drill a pilot hole before driving in a lag bolt. This prevents the wood from splitting and makes installation easier. The pilot hole should be slightly smaller than the shank of the bolt but larger than the thread core. Consult a drilling chart for the correct size based on your bolt diameter and wood type.Step 2: Driving the Lag BoltUse a wrench or socket to drive the lag bolt into the pre-drilled hole. Apply steady, even pressure. Avoid over-tightening, which can strip the threads or damage the wood. Using a washer under the head can distribute the pressure and prevent the bolt head from sinking into the wood.Step 3: Ensuring a Secure HoldTest the connection to ensure it is secure. If the bolt spins freely, it may be stripped. In this case, you may need to use a longer or thicker bolt, or insert a wood plug and try again.Applications of Lag Bolts in WoodworkingDeck ConstructionLag bolts are commonly used in deck construction to secure the ledger board to the house and to fasten the deck frame together.Framing and Timber FramingLag bolts are essential for joining large timbers in framing and timber framing projects. They provide a strong, reliable connection.Furniture MakingWhile less common in fine furniture making, lag bolts can be used in larger, more robust furniture pieces where strength is a priority.Factors to Consider When Buying Lag BoltsLoad RequirementsConsider the amount of weight the lag bolts will need to support. Consult engineering tables to determine the appropriate size and spacing for your specific application. Over-engineering is generally better than under-engineering.Environmental ConditionsIf the project will be exposed to moisture or corrosive elements, choose stainless steel or galvanized lag bolts.Wood TypeDifferent types of wood have different densities and holding power. Softer woods require larger diameter lag bolts or deeper penetration.Where to Buy Lag Bolts for WoodLocal Hardware StoresLocal hardware stores offer a convenient way to purchase lag bolts. You can inspect the bolts in person and get advice from store staff.Online RetailersOnline retailers offer a wider selection of lag bolts at competitive prices. Buying lag bolts for wood online allows you to compare different brands, materials, and sizes easily. Be sure to check reviews and confirm the specifications before making your purchase.Specialty Fastener SuppliersSpecialty fastener suppliers like Hebei Muyi Import&Export Trading Co.,Ltd offer a wide range of specialized lag bolts and can provide expert advice on choosing the right fasteners for your project.Troubleshooting Common IssuesStripped ThreadsIf the threads of the lag bolt strip, try using a longer bolt or a bolt with a larger diameter. You can also try inserting a wood plug into the hole and then re-drilling a pilot hole.Splitting WoodSplitting wood is usually caused by not pre-drilling a pilot hole or using a pilot hole that is too small. Use the correct size pilot hole for the diameter of the bolt and the type of wood.Difficulty Driving the BoltDifficulty driving the bolt can be caused by a pilot hole that is too small or wood that is too dense. Try using a larger pilot hole or lubricating the bolt with wax.Lag Bolt Strength Chart ExampleThe following table shows approximate withdrawal strength for lag screws in different wood densities. These values are for illustrative purposes only. Always consult engineering tables and local building codes for specific requirements. Wood Density Lag Screw Diameter (inches) Approximate Withdrawal Strength (lbs/inch of penetration) Softwood (e.g., Pine) 1/4' 200 Softwood (e.g., Pine) 1/2' 800 Hardwood (e.g., Oak) 1/4' 400 Hardwood (e.g., Oak) 1/2' 1600 *Note: These values are estimates. Always consult engineering tables for accurate values.ConclusionBuying lag bolts for wood requires careful consideration of size, material, and application. By understanding the different types of lag bolts and following the installation guidelines, you can ensure a strong and secure connection for your woodworking projects. Whether you're building a deck, framing a house, or creating sturdy furniture, choosing the right lag bolts is essential for success.Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only. Always consult with a qualified professional for specific advice related to your project.Reference: Data parameters above are obtained from the official website data. Please refer to the official website for the latest information.













Please enter your email address and we will reply to your email.